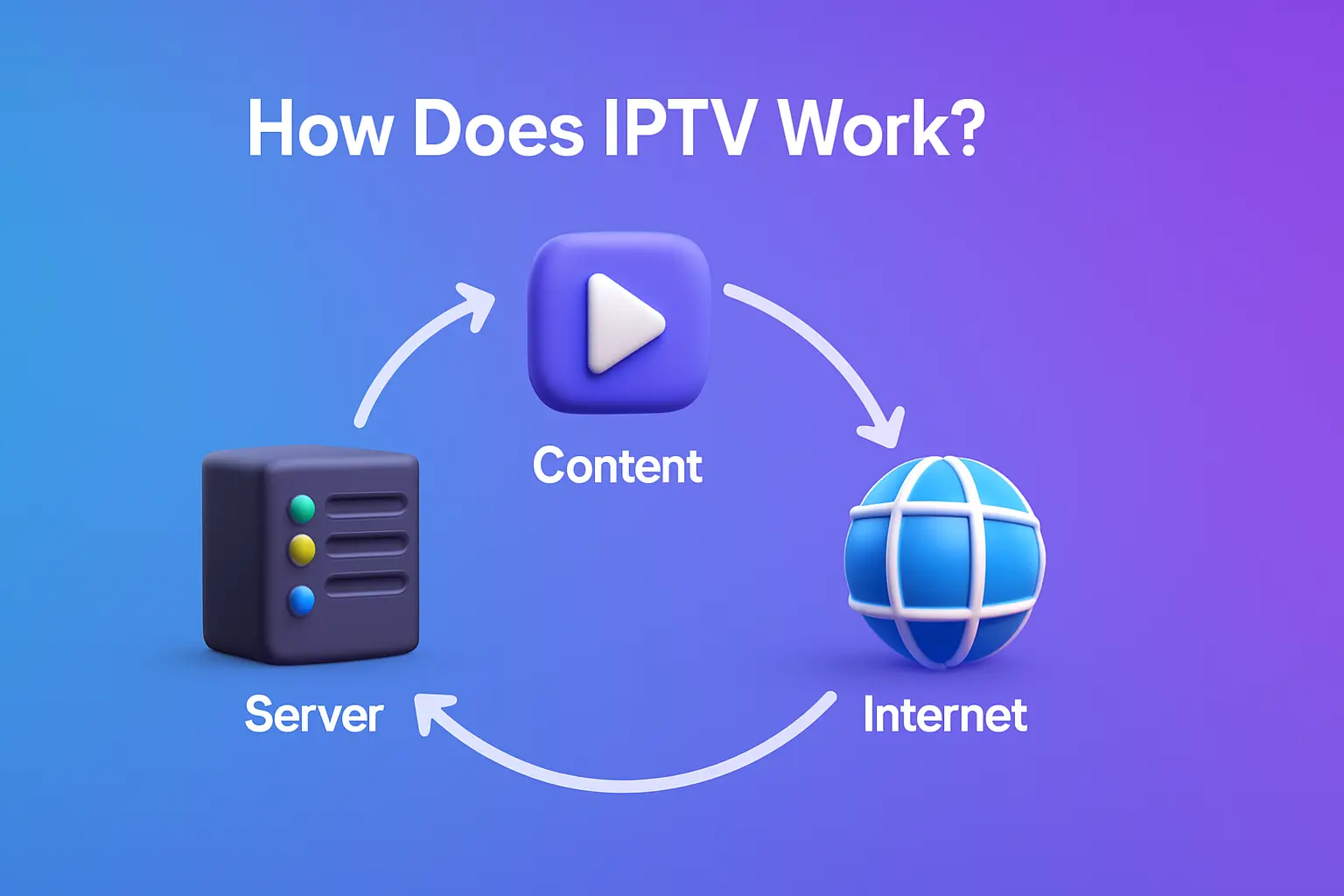
IPTV works by streaming TV content over your internet connection. It relies on a complex architecture of servers, encoding systems, and IP networks to deliver programming. The process involves compressing video into data packets and transmitting them via fiber-optic networks to your IPTV box, which decodes the packets for viewing.
IPTV Subscription services offer live TV, video on demand, and time-shifted options, providing a more flexible and personalized viewing experience compared to traditional cable or satellite TV. Keep exploring to uncover the benefits of this innovative technology.
The Fundamentals of IPTV Technology
IPTV, or Internet Protocol Television, is a cutting-edge technology that leverages the power of the internet to deliver television content directly to viewers’ devices. It encodes video and audio content into compressed data packets, which are then transmitted over an IP network to the viewer’s set-top box or smart TV.
The IPTV system comprises content sources, encoding and encryption systems, and distribution servers that work together to ensure seamless streaming. Unlike traditional broadcasting methods that rely on cable or satellite signals, IPTV utilizes internet protocols to deliver content.
This innovative approach enables viewers to access a wide range of programming options, including live TV, video-on-demand, and personalized recommendations, catering to their diverse preferences and enhancing the overall viewing experience.
Content Delivery Process in IPTV
The content delivery process is at the heart of IPTV’s functionality, ensuring that video and audio content reaches viewers’ devices seamlessly. IPTV service providers store the content on servers and use video compression to convert it into data packets.
These packets are then transmitted over fiber-optic networks to a content delivery network. Upon user requests, the data packets are divided into IP packets and delivered to the viewer’s IPTV box or compatible device via IP multicast technology. This allows for efficient distribution of live TV channels and video-on-demand content to multiple viewers simultaneously.
The IPTV box decodes the IP packets, converting them into a format compatible with the viewer’s television, enabling them to watch the content without interruption.
Types of IPTV Services
Several distinct types of IPTV services exist, each catering to different viewer preferences and consumption habits. Live TV offers real-time access to television channels, while Video on Demand (VOD) allows streaming of on-demand content from a pre-recorded library.
Time-Shifted TV enables watching previously aired programs at your convenience. Transactional VOD (TVOD) follows a pay-per-view model, Subscription VOD (SVOD) requires a monthly fee, and Advertising-supported VOD (AVOD) provides free content with ads.
These services deliver personalized entertainment experiences, from live events to on-demand shows and movies, giving you greater control over your viewing. Understanding the differences between these IPTV service types helps you choose the best option for your needs, whether you prefer scheduled programming or the flexibility of on-demand content.
Comparing IPTV With Traditional TV Broadcasting
While both IPTV and traditional TV broadcasting deliver video content to viewers, they differ significantly in their content delivery methods and viewing capabilities. IPTV uses Internet Protocol (IP) technology to stream content over the internet, requiring a broadband Internet connection from an internet service provider.
In contrast, traditional cable and satellite TV rely on dedicated cable television formats and digital television signals. The key differences between IPTV and traditional TV include:
1. Content delivery: IP-based streaming vs. cable or satellite signals
2. Viewing options: On-demand and time-shifted vs. real-time broadcasts
3. Personalization: Integration with online services vs. limited external content
4. Dependency on internet: Requires stable, high-speed access vs. less reliant on internet quality
IPTV’s unique features set it apart from traditional TV broadcasting.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is IPTV Legal in the USA?
IPTV’s legality in the USA depends on content licensing and regulatory oversight. Consider legal implications, ISP restrictions, and consumer protection when exploring alternative viewing options. Ensure your subscription service complies with national broadcasting laws to avoid disputes.
What Do You Need for IPTV to Work?
To set up IPTV, you’ll need a high-speed internet connection, a compatible streaming device, and a subscription from an IPTV provider offering your desired channels. The provider’s app will deliver the content to your device.
How Much Is IPTV per Month?
IPTV monthly subscription fees vary based on bundled streaming packages and premium channel selections. Expect to pay $10-$40 for basic plans, $50-$100 for premium. Providers offer cost-effective pricing models, pay-per-view options, and flexible terms for multi-device access.
How Does IPTV Work Technically?
To deliver IPTV, you’ll need robust network infrastructure and optimized bandwidth usage. Employing efficient content delivery protocols, compatible devices, and secure encryption is crucial. Multicasting improves performance, while advanced codecs and user-friendly interfaces enhance the viewing experience.